
Manual Gas Transfer Pump: A Comprehensive Guide
Manual siphon pumps efficiently transfer liquids using gravity and pressure‚ eliminating the need for electricity; mastering their use involves proper submersion and suction control.
Today’s date is 12/24/2025 10:29:21 ()‚ and accessing downloadable manuals provides crucial safety details‚ warranty information‚ and regulatory compliance.
What is a Manual Gas Transfer Pump?
A manual gas transfer pump‚ often referred to as a siphon pump‚ is a hand-operated device designed for moving liquids from one container to another without relying on electricity. These pumps utilize a simple yet effective mechanism based on atmospheric pressure and gravity to initiate and sustain fluid flow.
Unlike electric pumps‚ manual versions offer portability and convenience‚ making them ideal for situations where power sources are unavailable or impractical. They are commonly employed for transferring fuels‚ water‚ or other non-corrosive liquids. The core principle involves creating a pressure differential – reducing pressure at the intake end and increasing it at the discharge end – to draw the liquid through the tubing.
Effectively‚ these pumps are a testament to simple engineering‚ providing a reliable solution for various liquid transfer needs‚ as highlighted by their efficient operation and ease of use.
How Manual Gas Transfer Pumps Work: The Siphon Principle
The siphon principle governs the operation of manual gas transfer pumps‚ leveraging atmospheric pressure and gravity. Initially‚ the pump needs priming – removing air from the tubing – to establish a continuous liquid column. Once primed‚ atmospheric pressure pushes the liquid up into the tube from the source container.
Simultaneously‚ gravity pulls the liquid down the discharge side‚ creating a pressure difference. This difference sustains the flow as long as the intake remains submerged and the discharge point is lower than the source. Repeated squeezing of a bulb‚ as seen in many models‚ initiates this suction.
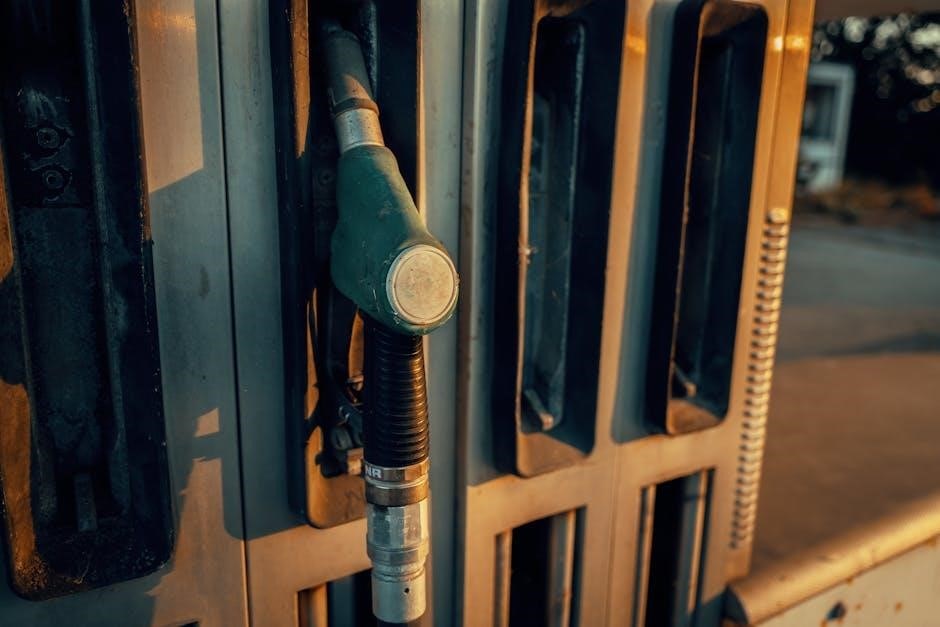

Essentially‚ the pump doesn’t “pull” the liquid; it creates a pathway where atmospheric pressure and gravity do the work‚ offering an efficient‚ electricity-free transfer method.
Key Components of a Manual Gas Transfer Pump
A typical manual gas transfer pump comprises several essential components working in unison. These include a rigid intake tube‚ designed for insertion into the liquid source‚ and a flexible discharge tube for directing the flow to the destination container.
Many pumps feature a squeeze bulb or similar mechanism to initiate suction‚ overcoming initial air resistance. Valves‚ often integrated within the pump housing‚ ensure unidirectional flow‚ preventing backflow. The pump housing itself provides structural support and often incorporates a control mechanism.

Material selection is crucial; components must be compatible with the transferred liquid to prevent corrosion or degradation‚ ensuring safe and reliable operation.
Types of Manual Gas Transfer Pumps
Manual gas transfer pumps aren’t a one-size-fits-all solution; several types cater to diverse needs. Self-priming manual pumps are designed to initiate flow with minimal user effort‚ often utilizing a built-in mechanism to create initial suction. These are convenient for frequent use and various liquid viscosities.
Hand-operated siphon pumps‚ conversely‚ rely entirely on manual action – typically squeezing a bulb – to establish the siphon effect. These are generally simpler in design and cost-effective for occasional transfers.
The choice between these depends on the frequency of use‚ the liquid’s properties‚ and the desired level of convenience.
Self-Priming Manual Pumps
Self-priming manual pumps excel in situations demanding quick and effortless liquid transfer. Unlike standard siphon pumps‚ they minimize the need for initial manual suction‚ employing internal mechanisms – often a check valve system – to draw fluid automatically. This feature proves invaluable when dealing with liquids that are difficult to siphon conventionally.
These pumps are particularly beneficial for users who require frequent transfers or struggle with the manual priming process. Their design ensures a consistent flow once initiated‚ reducing user fatigue and improving efficiency. They are a reliable choice for various applications.
Hand-Operated Siphon Pumps
Hand-operated siphon pumps represent a classic and straightforward approach to liquid transfer‚ relying on manual bulb squeezing to initiate and maintain flow. These pumps utilize the siphon principle‚ creating suction to draw liquid from a source container to a lower destination. They are incredibly versatile and require no external power source‚ making them ideal for portable applications.

Operation involves repeatedly compressing the bulb‚ establishing a vacuum that lifts the fluid. Monitoring the transfer is crucial to prevent spills and ensure a controlled process. Their simplicity and affordability make them a popular choice for tasks like fuel transfer and aquarium maintenance.
Applications of Manual Gas Transfer Pumps
Manual gas transfer pumps find diverse applications due to their portability and ease of use. Automotive fuel transfer is a common use‚ allowing for safely moving gasoline or diesel from containers to vehicles‚ especially in emergency situations. Aquarium maintenance benefits greatly‚ enabling water changes and gravel cleaning without disturbing the ecosystem.

Furthermore‚ these pumps are invaluable for emergency fuel transfer‚ providing a lifeline when access to traditional fueling methods is limited. Their self-contained nature makes them suitable for remote locations or situations where electricity isn’t available. They are also used in various DIY projects and fluid handling tasks.
Automotive Fuel Transfer
Manual gas transfer pumps are exceptionally useful for automotive fuel transfer‚ offering a safe and controlled method for moving gasoline or diesel. This is particularly valuable when a vehicle is out of fuel and a fuel container is the only source available. The pumps allow for precise fuel delivery‚ minimizing spills and potential hazards.
They are ideal for situations where access to a gas station is limited‚ such as in remote areas or during emergencies. Utilizing a manual pump eliminates the risk associated with siphoning by mouth‚ a dangerous practice. Proper grounding and adherence to safety precautions are crucial during fuel transfer to prevent static discharge.
Aquarium Maintenance
Manual gas transfer pumps‚ specifically siphon pumps‚ are invaluable tools for routine aquarium maintenance; They facilitate water changes by safely and efficiently removing water from the tank without disturbing the gravel or decorations. This method is gentler on fish and invertebrates compared to forceful vacuuming.
These pumps are also excellent for gravel cleaning‚ allowing you to remove debris and waste buildup. The controlled suction prevents the accidental removal of small fish or shrimp. Utilizing a siphon pump ensures a cleaner and healthier environment for aquatic life‚ contributing to their overall well-being. Regular water changes are essential for maintaining optimal water quality.
Emergency Fuel Transfer

Manual gas transfer pumps offer a crucial solution for emergency fuel transfer situations‚ particularly when electricity is unavailable. Whether dealing with a stranded vehicle or needing to redistribute fuel from a generator‚ these pumps provide a reliable‚ self-contained method for moving flammable liquids.
Their operation doesn’t rely on external power sources‚ making them ideal for remote locations or disaster scenarios. However‚ strict adherence to safety precautions is paramount when handling flammable materials. A manual pump allows for controlled transfer‚ minimizing the risk of spills and potential hazards. This capability provides peace of mind during critical times.
Safety Precautions When Using a Manual Gas Transfer Pump
Handling flammable liquids with a manual gas transfer pump demands strict adherence to safety protocols. Always work in a well-ventilated area‚ away from open flames or ignition sources. Ground both containers – the source and the receiving vessel – to prevent static electricity buildup‚ a potential ignition hazard.
Avoid overfilling containers‚ leaving space for expansion. Inspect the pump for any damage before use‚ ensuring all connections are secure. Never smoke while transferring fuel. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby and familiarize yourself with its operation. Review the pump’s manual for specific safety guidelines and warnings.
Flammable Liquids Handling
Transferring flammable liquids like gasoline requires extreme caution. Always operate the manual gas transfer pump outdoors or in a remarkably well-ventilated space‚ eliminating any potential for vapor accumulation. Grounding both containers – source and destination – is paramount to dissipate static electricity‚ preventing sparks.
Avoid using plastic containers not specifically designed for fuel storage. Never smoke or allow open flames nearby. Inspect the pump thoroughly for leaks or damage before each use. Have a Class B fire extinguisher readily accessible‚ and understand its proper operation. Consult the pump’s manual for detailed safety instructions specific to flammable liquid transfer.

Avoiding Static Electricity
Static electricity poses a significant risk when transferring flammable liquids with a manual gas transfer pump. The flow of liquid itself can generate static‚ potentially igniting vapors. Grounding is the primary preventative measure; securely connect both the source and receiving containers to a known earth ground using a grounding wire.
Avoid transferring liquids on dry‚ windy days‚ as these conditions exacerbate static buildup. Use conductive hoses rather than non-conductive plastic ones. Regularly inspect grounding connections to ensure their integrity. Slowing the flow rate can also reduce static generation. Always prioritize safety and consult the pump’s manual for specific grounding recommendations.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Manual Gas Transfer Pump
Begin by securely positioning the intake tube into the source container‚ ensuring it’s fully submerged. Place the discharge tube into the receiving container‚ keeping it lower than the source liquid level. Repeatedly squeeze the pump’s bulb to initiate suction – this creates the necessary pressure difference.
Monitor the flow closely‚ adjusting the bulb’s squeezing as needed to maintain a steady transfer. Avoid over-squeezing‚ which can cause splashing. Once the transfer is complete‚ remove the intake tube first to prevent backflow. Always refer to the pump’s manual for specific instructions and safety precautions.
Priming the Pump: Creating Initial Suction
Priming is crucial for initiating liquid flow with a manual siphon pump. Begin by ensuring both tubes are securely connected and the intake tube is fully submerged in the liquid. Repeatedly squeeze the pump’s bulb; this action evacuates air from the system‚ creating a vacuum.
Continue squeezing until liquid begins to draw up the intake tube. Once liquid reaches the pump and flows towards the discharge tube‚ maintain a consistent squeezing rhythm. Remember‚ proper priming establishes the pressure differential needed for efficient transfer. Consult the manual for specific priming techniques related to your pump model.
Maintaining Your Manual Gas Transfer Pump
Regular maintenance ensures the longevity and optimal performance of your manual gas transfer pump. After each use‚ thoroughly flush the pump and tubes with a compatible solvent to remove any residual liquid‚ preventing clogging and corrosion.
Store the pump in a clean‚ dry environment‚ away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Inspect hoses for cracks or wear‚ replacing them as needed. Download the pump’s manual for detailed cleaning instructions and troubleshooting tips. Addressing minor issues promptly prevents larger problems‚ guaranteeing reliable operation for years to come.
Cleaning and Storage
Proper cleaning after each use is vital for maintaining your manual gas transfer pump. Flush the pump and hoses thoroughly with a solvent compatible with the transferred liquid to eliminate residue and prevent corrosion. Pay close attention to the intake and discharge tubes‚ ensuring they are completely clear.
For storage‚ ensure the pump is dry and clean. Store it in a cool‚ dry place‚ shielded from direct sunlight. Refer to the pump’s manual for specific storage recommendations. Correct cleaning and storage significantly extend the pump’s lifespan and guarantee optimal performance when needed.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If the pump fails to prime‚ verify the intake tube is fully submerged and free of obstructions. Repeatedly squeeze the bulb to initiate suction‚ ensuring a tight seal. A lack of flow might indicate a blockage within the hose or pump itself; inspect and clear any debris.
Slow transfer rates could stem from a partially blocked hose or insufficient priming. Always consult the manual for specific troubleshooting steps related to your pump model. Remember to prioritize safety and discontinue use if issues persist‚ seeking professional assistance if necessary.
Choosing the Right Manual Gas Transfer Pump
Selecting the appropriate pump hinges on the liquid’s compatibility with the pump’s materials – ensure resistance to corrosion or degradation. Consider the flow rate needed for your application; higher rates demand pumps with larger diameter hoses and efficient siphon mechanisms.
Evaluate the viscosity of the fluid‚ as thicker liquids require more powerful pumps. Prioritize pumps with robust construction for durability‚ especially for frequent or heavy-duty use. Always refer to the pump’s specifications and user manual to confirm suitability for your intended purpose‚ ensuring safe and effective operation.
Material Compatibility
Crucially‚ assess the pump’s materials against the liquid being transferred; incompatibility can lead to corrosion‚ degradation‚ or even pump failure. For fuels‚ select pumps with Viton or Teflon components‚ known for their chemical resistance. Avoid pumps with rubber parts if transferring solvents‚ as they can dissolve and contaminate the fluid.
Polypropylene and polyethylene are suitable for many liquids‚ offering good all-around resistance. Always consult the pump manufacturer’s chemical compatibility chart to verify suitability. Prioritizing compatible materials ensures longevity‚ prevents contamination‚ and maintains safe operation during fluid transfer.
Flow Rate Considerations
Determining the required flow rate is vital for efficient transfer; consider the volume of liquid and the time available. Manual pumps generally offer lower flow rates than electric options‚ making them best suited for smaller volumes or situations where speed isn’t critical.
Pump diameter and siphon tube length significantly impact flow; wider tubes and shorter lengths facilitate faster transfer. Repeated squeezing of the bulb (in bulb-style pumps) also influences the rate. Evaluate your needs carefully to select a pump capable of delivering the desired flow without excessive effort or time.
Manuals and Documentation: Where to Find Them
Accessing comprehensive manuals is crucial for safe and effective pump operation. Manufacturers’ websites are primary sources‚ often offering downloadable PDFs containing detailed instructions‚ safety precautions‚ and warranty information. Retailer websites‚ where the pump was purchased‚ may also host digital copies.
Look for documentation covering proper priming techniques‚ maintenance schedules‚ and troubleshooting guides. Specific model numbers are essential for locating the correct manual. Remember that manuals often include FCC rules and compliance details. Downloading these resources ensures you have readily available support for your manual gas transfer pump.
Comparing Manual Pumps to Electric Transfer Pumps
Manual gas transfer pumps offer simplicity and portability‚ requiring no electricity – ideal for remote locations or emergencies. Electric pumps‚ conversely‚ provide significantly faster flow rates and reduced physical effort‚ making them suitable for large-volume transfers.

Cost-effectively‚ manual pumps are generally cheaper upfront‚ but electric pumps may save time and labor in the long run. Maintenance is typically simpler for manual pumps‚ while electric models require battery or power source considerations. Choosing between the two depends on transfer frequency‚ volume‚ and available resources.
The Future of Manual Gas Transfer Technology
Innovations in materials science could lead to lighter‚ more durable manual pumps with improved chemical resistance. Ergonomic designs are likely to enhance user comfort and reduce fatigue during operation‚ addressing a key limitation of current models.
Integration of self-priming mechanisms and flow control valves could further streamline the transfer process. Smart features‚ such as flow rate indicators‚ are conceivable‚ though maintaining simplicity will be crucial. Despite the rise of electric pumps‚ a continued demand exists for reliable‚ off-grid solutions‚ ensuring a future for refined manual gas transfer technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How do I start a siphon? A: Ensure both tubes are submerged; repeatedly squeeze the bulb to initiate suction‚ then monitor the flow. Q: Can I use this with any liquid? A: Check material compatibility – some pumps aren’t suitable for corrosive substances.
Q: What if the flow stops? A: Reprime the pump‚ ensuring a clear intake and discharge path. Q: Where can I find the pump manual? A: Downloadable manuals are often available online‚ providing safety and warranty details. Q: Is this safer than electric pumps? A: Manual pumps eliminate electrical hazards‚ but flammable liquid handling requires caution.
Manual gas transfer pumps‚ often siphon-based‚ offer a simple solution for moving liquids without electricity‚ relying on gravity and atmospheric pressure for efficient operation. These pumps excel in scenarios demanding portability and safety‚ like automotive fuel transfer or aquarium maintenance.
Understanding the siphon principle – creating suction via a submerged intake and lower discharge point – is key to successful use. Today‚ 12/24/2025‚ accessing detailed manuals is crucial for safe operation‚ covering warranty details and regulatory compliance. Proper technique ensures effective and spill-free liquid transfer.